This article provides you with a brief overview of the trends that will determine mortgage interest rates. Ultimately, the decision on whether to apply for a mortgage loan depends on the borrower’s financial circumstances and credit score.
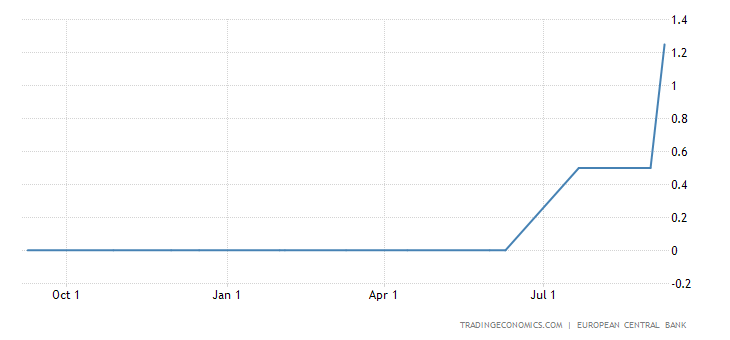
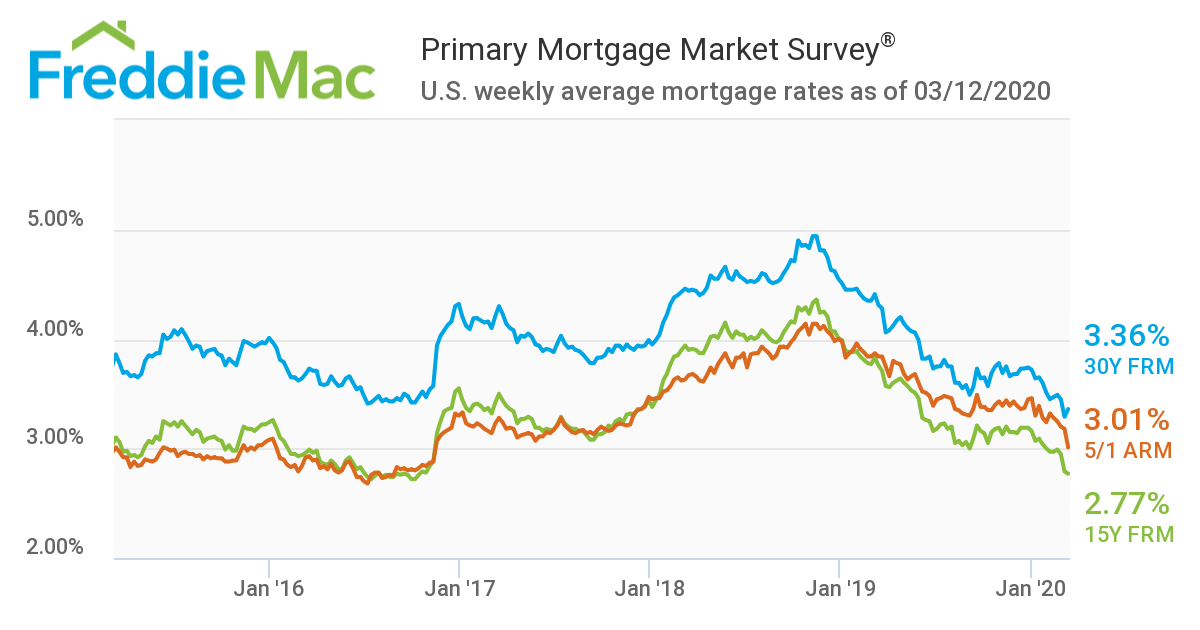
Interest rates for mortgages have been at historic lows for much of the last decade
After years of historically low mortgage rates, the market is finally starting to catch up. Mortgage rates peaked in the mid-4% range at the start of the decade, then continued their decline throughout the next two decades. Then, in March 2022, the Federal Reserve announced it would begin raising its federal funds rate. This action is expected to push mortgage rates upwards several times throughout the year.
While higher rates may signal a stronger economy, they will also increase the cost for homebuyers. Despite this trend, mortgage rates remain historically low, and homebuyers continue to reap the benefits of low mortgage rates. In fact, recent interest rate hikes have been attributed to U.S. government debt, as global banks continue to reverse policies that have kept rates low.
They will continue to rise in 2022
The Federal Open Market Committee is set to meet this month and will decide on the next hike in interest rates. Many experts believe rates will stay the same or rise a bit more in 2022. The Mortgage Report has predicted that mortgage rates will continue to increase, citing high consumer spending and inflationary pressure. While the influenza pandemic may have had a limited impact on the mortgage market, the high inflation rate indicates that the FED is serious about aggressive rate hikes.
According to the Fannie Mae housing forecast, mortgage interest rates will stabilize in the second half of 2022 and remain relatively low in the first three quarters. However, mortgage rates in the fives will likely slow down housing demand and affect entry-level homebuyers. However, Freddie Mac expects the 30-year fixed-rate mortgage to average 4.6% in 2022 and rise to 5.0% in the fourth quarter.
They are influenced by inflation
Inflation affects mortgages and other forms of consumer debt, but it also influences the interest rates for short-term loans, auto loans, and personal loans. The federal funds rate, or prime rate, may rise to offset inflation or temper the effects of rising costs. On the other hand, a low prime rate may promote borrowing and consumer spending. It is important to keep these things in mind when looking at the latest trend.
Inflation is a metric used to measure changes in the cost of goods and services. Inflation affects the amount of money that people can spend, while decreasing their purchasing power. When interest rates are low, the consumer gains and the lender loses. While the two factors are not directly linked, they are often correlated. While it is impossible to say that the two are directly correlated, it is helpful to understand how inflation affects mortgage interest rates.
They are influenced by geopolitical events
The interest rates for mortgages are influenced by many factors, including incoming data from the economy and the stock market, as well as geopolitical events like the recent war in Ukraine. Although the current interest rate environment is murky, recent events, such as the Russian invasion of Ukraine, have caused energy prices to rise significantly. Adding to the confusion is media reporting that can make borrowers assume that interest rates are at zero.
They are influenced by bond prices
Mortgage rates are closely linked to inflation expectations. Other factors such as the stock market can also affect mortgage rates. However, the most common factor is the price of mortgage-backed bonds, which are issued by mortgage lenders and backed by the interest paid by mortgage holders. As interest rates rise, bond prices decrease and vice versa. Therefore, a rise in bond prices will affect mortgage rates in the opposite direction. Therefore, it is important to understand how bond prices affect mortgage rates.
The Fed sets interest rates, and when the Federal Reserve raises their target interest rate, bonds’ prices tend to drop. Although investors worry about this rise in interest rates, this is not necessarily a bad thing. Rising rates are beneficial for bond holders because they allow them to compound their interest. Bond prices can drop even if the economy is growing, so they should not be discouraged. The only problem with rising interest rates is that it causes inflation.
They are influenced by unemployment levels
As the economy improves, so will mortgage rates. A good jobs report can help lower rates, and a bad one can increase them. But the job market is not just about unemployment; the Fed also manipulates rates to encourage more homebuyers. Here are some reasons why unemployment levels are important to mortgage rates. They may surprise you! This information is not a complete picture of mortgage rates, but it can be a helpful guide.
The Fed sets target ranges for inflation and unemployment. When unemployment is low, the Fed raises interest rates to spur the economy. Higher rates slow the economy and cause businesses and consumers to borrow less. Homebuyers may only be able to afford a smaller loan than they would have otherwise. Unemployment also causes homeowners to spend less, since they have less equity in their homes. When unemployment is high, it can lower interest rates for people who can’t qualify for a mortgage or refinance their mortgage.
 “Homeownership Nightmare: Grant Cardone Reveals the Shocking Truth!”
“Homeownership Nightmare: Grant Cardone Reveals the Shocking Truth!”